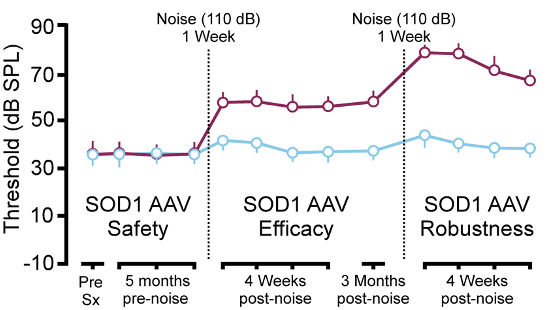
SOD1 gene therapy (blue) shows a persistent neuroprotective effect compared to the severe hearing loss observed in the control animals (purple)
Invention Summary:
Hearing loss is the third most common chronic health problem in the United States, with noise-induced hearing loss effecting nearly 1 out of every 4 adults (over 60M). Inner ear hearing damage is prevalent from recreational and occupational noise exposures, like music concerts, construction sites, factory settings, and military jobs. Such acoustic traumas are the cause of noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) as it leads to injury of the hair cells in the inner ear by an increase of oxidative stress. Even with the present risk in a large portion of the population and its association with aging, there are no effective measures for long term prevention of NIHL.
Researchers at Rutgers University have developed an adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based gene therapy for prevention and treatment of NIHL. The team shows that they can successfully target the expression of antioxidative enzyme SOD1 in the inner ear. Using animal models, the inventors show that expression of SOD1 acts as a neuroprotectant, preventing the loss of hair cells after exposure to high-intensity sounds. Overall, this technology opens a new venue for treatment of hearing loss caused by external agents and, at the same time, a preventative therapy that is essential for many occupations.
Market Applications:
- Preventative and treatment of acute and chronic hearing loss/damage
Advantages:
- Gene therapy for neuroprotection against noise exposure
- Targeted gene delivery to the inner ear using AAV system
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Provisional patent application filed, patent pending. Available for licensing and/or research collaboration. Please contact marketingbd@research.rutgers.edu