Invention Summary:
Currently there is no effective therapy for prevention or treatment of radiation therapy-induced gastrointestinal (GI) tract injury This is also true for Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) which remains a major complication after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, a widely-used therapy for hematologic malignancies and blood disorders.
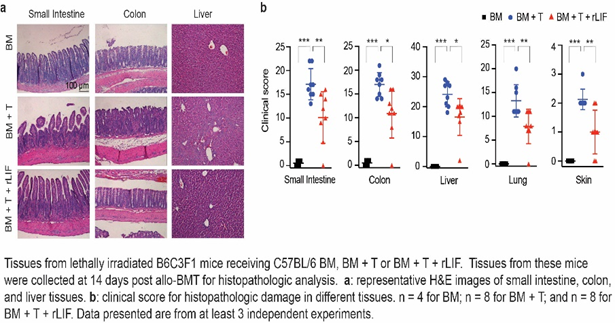
Rutgers researchers discovered that leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), a naturally occurring cytokine, present in the intestinal stem cells and is critical in maintaining intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and regeneration. They highlight an unexpected role of LIF in protecting against radiation therapy-induced GI tract injury and GVHD development. Findings in mice suggest that LIF could protect the GI tract from injuries leading to: (1) 50% higher regeneration of intestinal epithelium after irradiation compared to controls, (2) less systemic symptoms such as weight loss, and (3) remarkably higher overall survival. Administrating recombinant LIF protein (rLIF) protects mice from GVHD-induced tissue damage and lethality without compromising the graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) activity, which is crucial to prevent tumor relapse. Different mouse models were tested as well as the potential mechanisms elucidated indicating that rLIF can reduce donor immune cell infiltration and activation and protect intestinal stem cells to ameliorate GVHD.
Market Applications:
- Radiation or chemotherapy induced gut syndrome
- Graft versus host disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease
- Treating other diseases where intestinal epithelium regeneration is lacking
Advantages:
- Highly efficacious protection of the intestinal epithelium
- Prolonged overall survival in vivo
- Potential efficacy in multiple indications
- Provides potential effective therapeutic strategy to limit tissue pathology without loss of anti-leukemic efficacy
Intellectual Property & Development Status:
Patent pending. Available for licensing and/or research collaboration.