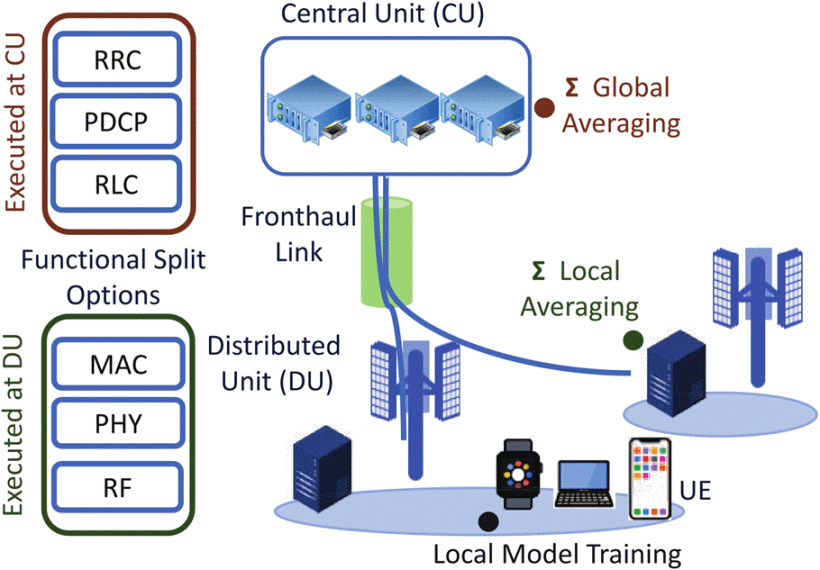
Fig. 1: Structure of federated learning-based NG-RAN algorithm.
Invention Summary:
Mobile network operators are faced with meeting demands beyond 5G networks, such as opening/virtualizing radio access network (RAN) layers, maintaining privacy, and achieving ultra-low latencies, high data rates, and low operational expenses for data transmission. Next generation RAN (NG-RAN) is a current solution to achieve flexibility and efficiency using the next generation fronthaul interface (NGFI) standard. However, the issue remains that fronthaul traffic must be reduced and privacy must be secured to prevent bottlenecking and support large-scale NG-RAN deployment.
Rutgers researchers developed a federated learning (FL)-based NG-RAN algorithm (“FedNG”) that allows user equipment and NG-RAN infrastructures to cooperatively collaborate throughout the learning process for a shared prediction model that ensures privacy and reduces the fronthaul interface burden. FL is one method to collaboratively train a machine learning model privately, without publishing original data streams to third-party applications. FedNG, compared to the existing federated averaging (FedAvg) model, demonstrated significantly improved performance using 3 real-world datasets in accuracy, service latency, and traffic size.
Market Applications:
• Efficient, flexible, and private machine learning algorithm for wireless mobile communication networks
Advantages:
• Privacy-preserving
• Low latency
• Cost-effective
• Avoids fronthaul interface bottlenecking (low traffic size)
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Available for licensing and/or research collaboration. For any business development and other collaborative partnerships contact marketingbd@research.rutgers.edu.
Publications: A. Younis, C. Sun and D. Pompili, "Communication-efficient Federated Learning Design with Fronthaul Awareness in NG-RANs," 2022 IEEE 19th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Smart Systems (MASS), Denver, CO, USA, 2022, pp. 599-605, doi: 10.1109/MASS56207.2022.00089