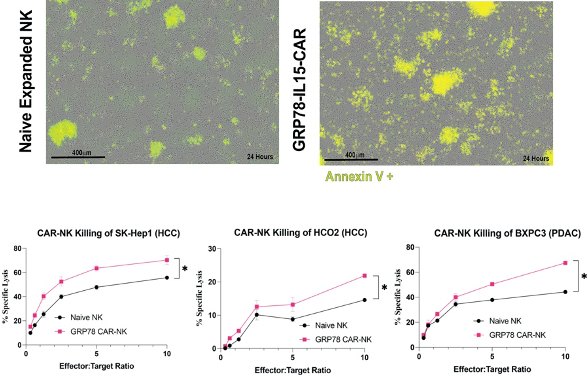
Incucyte Killing Assay Images with AnnexinV cell death signal in MKI-Resistant HCC (Top panel). Chromium-51 release assays comparing GRP78 CAR-NK Killing to Naïve NK killing of various MKI-resistant tumor cell lines (bottom panels). Values shown are Means ± SEM. Significant p values indicated in red.
Invention Summary:
CAR-NK therapies have minimal toxicities compared to CAR-T therapy. Heat shock proteins (HSP), such as Glucose Regulated Protein 78 (GRP78), are valuable targets to treat cancers. GRP78 is a protein-folding chaperone that resides in the endoplasmic reticulum in cells but is selectively expressed on the surface of acute myeloid leukemia cells as well as solid tumors. To date, there is no report of the combination therapy of HSP inhibitor and chemotherapeutic to enhance treatment with CAR-NK cells targeting GRP78.
Rutgers researchers have developed a combination therapy of HSP90 inhibitor and multikinase inhibitor with CAR-NK treatment. To improve GRP78 CAR-NK efficacy, a novel combination chemotherapy that combines the multikinase inhibitor, with HSP90 inhibitors. This combination therapy improves GRP78 surface expression in vitro with minimal toxicities to mice after short course of treatment. Strong killing of various GRP78-positive tumor cell lines by the GRP7-CAR with strong specificity for GRP78. In a MKIR-HCC xenograft NSG mouse model, the improved survival of the mice with minimal effects on mouse weight was observed.
Market Applications:
- Solid tumors with cell surface GRP78 protein.
- Acute myeloid leukemias.
Advantages:
- Compared to CAR-T, a GRP78-CAR-NK does not produce IL-6 which is associated with Cytokine Release Syndrome cytotoxicity.
- Low dosage and less toxic
- Utilizes a novel targeting sequence.
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Provisional patent application filed, patent pending. Available for licensing and/or research collaboration. For any business development and other collaborative partnerships contact marketingbd@research.rutgers.edu