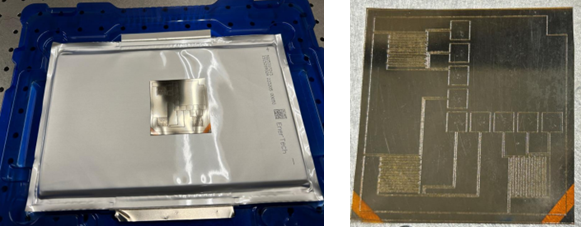

A flexible thin-film sensor is installed on a LIB cell for the thermal conductivity/diffusivity measurement. The sensor has patterns that can deposit heat and measure local temperature simultaneously.
Invention Summary:
The reliable measurement of a battery’s state of health (SOH) and state of charge (SOC) is critical in battery management systems for monitoring battery packs in electric vehicles, mobile phones, and many other devices. Open Circuit Voltage (OCV) is a general method to measure the SOC, but it is still challenging to apply to some cell chemistries that have a flat OCV curve, such as Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries.
Rutgers researchers have developed a novel flexible thin‐film sensor that can be adhered to the surface of individual battery cells and provide real‐time non‐invasive diagnosis of SOH and SOC of the battery cell by direct measurement of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity. This method is not affected by ambient temperature and measures independently of current, so it provides precise real-time measurement during cell charge or discharge. This technology can be a promising alternative for monitoring of SOH and SOC of individual cells.
Market Applications:
- Battery management system
- Lithium-ion battery manufacturing
- Lithium-ion battery recycling
- EV Battery monitoring
- Consumer electronics
Advantages:
- Not affected by ambient temperature
- Not dependent on the instantaneous cell current (Can be applied during cell charge or discharge)
- Provides real-time SOH monitoring on individual cells.
- Provide reliable SOC monitoring for LFP batteries
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Provisional patent application filed, patent pending. Available for licensing and/or research collaboration. For any business development and other collaborative partnerships, contact: marketingbd@research.rutgers.edu