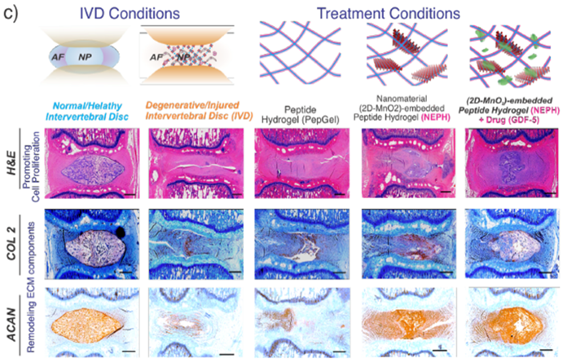
 Nanomaterial (2D-Mn02)-embedded peptide hydrogel (NEPH) promotes cellular proliferation and tissue regeneration.
Nanomaterial (2D-Mn02)-embedded peptide hydrogel (NEPH) promotes cellular proliferation and tissue regeneration.
Invention Summary:
The limited capacity for regeneration, the presence of pro-inflammatory factors, and the complex extracellular matrix (ECM) microenvironment of degenerated intervertebral discs (IVD) remain significant issues that must be addressed despite significant research to find effective treatments.
To overcome the issues outlined above, a team led by Rutgers, created an injectable peptide hydrogel utilizing nanomaterials that hierarchically self-assemble to form two-dimensional MnO2 nanosheet-peptide (FEFKFEFK) and one-dimensional peptide fibrils. This nano-hybrid peptide hydrogel stimulates IVD cell proliferation and can deliver pro-regenerative cytokines. According to current market research, there is an unmet market for injectable nanomaterial hydrogels, which require no surgical incisions, thus directly addressing the pathology of the underlying condition and reducing unwanted biological risks. .
Market Applications:
- Treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD).
- Tissue regeneration is various drug payloads.
- Spinal/central nervous system-related injuries.
- Human and Animal degenerative disc diseases.
Advantages:
- Injectable nanomaterial hydrogel.
- Metal Co-factor promotes proline-rich collagen recycling.
- Reduction in pain-related markers.
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Provisional filed. Patent pending. Available for licensing and/or search collaboration. For any business development and other collaborative partnerships contact: marketingbd@research.rutgers.edu