
Invention Summary:
APYs are novel, orally available compounds for treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacterial pathogens, fastidious Gram-negative bacterial pathogens, and some non-fastidious Gram-negative bacterial pathogens--including drug-resistant and multi-drug-resistant (MDR) strains.
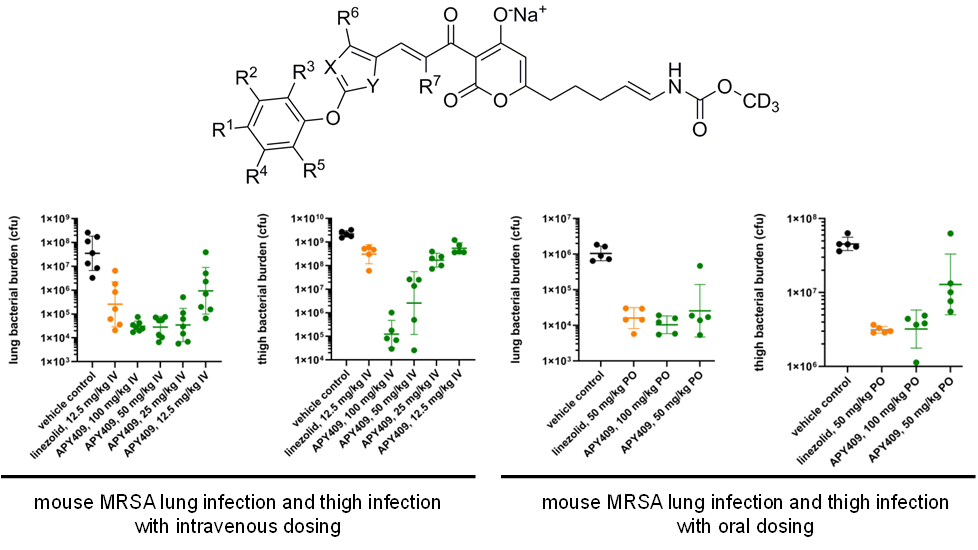
Our researchers have indicated that APYs exhibit potent in vitro antibacterial activity against all Gram-positive and all fastidious Gram-negative bacterial pathogens relevant to lower-respiratory-tract infections and skin-and-soft-tissue infections, including Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Enterococcus spp., Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Legionella pneumophila, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae; (MIC50s £ 0.78 mg/ml; MIC90s £ 1.56 mg/ml). APYs also exhibit in vitro antibacterial activity against the non-fastidious Gram-negative bacterial pathogens Acinetobacter spp. and Burkholderia spp. (MIC50s £ 3.13 mg/ml; MIC90s £ 6.25 mg/ml). APYs exhibits potent in vivo efficacy in a mouse MRSA lung-infection models (EDs = 12.5 mg/kg IV and 25 mg/kg PO) and in a mouse MRSA thigh‑infection model (ED = 50 mg/kg PO). APYs exhibit in vitro coverage and potency superior to the current oral standard of care linezolid and superior to the current intravenous‑only standards of care vancomycin and daptomycin. APYs exhibit in vivo efficacy equal to the oral current standard of care linezolid.
Market Applications:
- Oral treatment of drug-susceptible, drug-resistant, and multi-drug-resistant Gram-positive and fastidious Gram‑negative bacterial infections.
- Intravenous or intravenous/oral-stepdown treatment of drug-susceptible, drug-resistant, and multi-drug-resistant Gram-positive and fastidious Gram-negative bacterial infections.
Advantages:
- Coverage of all Gram-positive and all fastidious Gram-negative bacterial pathogens relevant to lower-respiratory-tract infections and skin-and-soft-tissue infections.
- Coverage superior to the current oral standard of care linezolid and the current intravenous‑only standards of care vancomycin and daptomycin.
- In vivo efficacy equal to the current oral standard of care linezolid.
- Novel binding site and novel mechanism.
- No cross-resistance with current antibacterial drugs.
- High oral availability.
- High safety margin.
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Issued US, EP, and Chinese patents and 12/2024 PCT patent filing. Available for licensing and/or research collaboration. This is a late-stage preclinical program with in vitro and in vivo proof of concept, ADME, safety pharmacology, PK, PK/PD, and exploratory toxicology (candidate-selection and de-risking stage). For business development or other collaborative partnerships, contact marketingbd@research.rutgers.edu