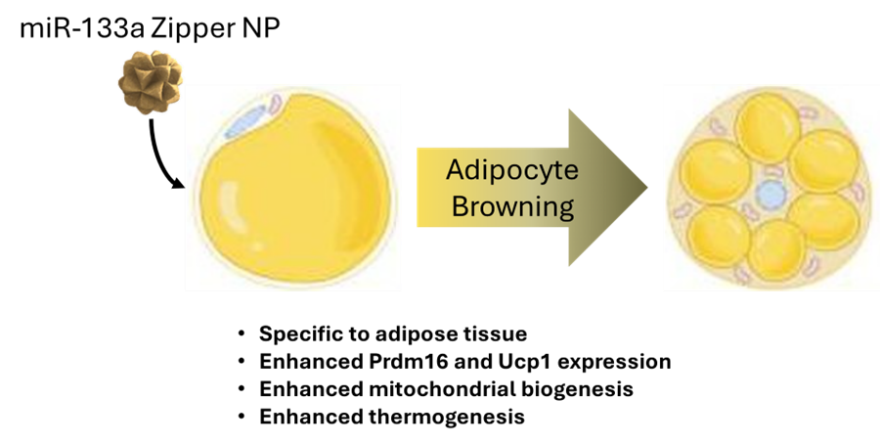
Introduction of a promising anti-obesity novel MiR-133a, Zipper nanoparticle treatment results in enhanced Prdm16 and Ucp1 expression, resulting in adipocyte browning.
Invention Summary:
Over 40% of adults are overweight and over 15% of adults are living with obesity. Obesity is a major contributor to various causes of mortality including cardiovascular disease, cancer, etc. Recently, a series of glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists, such as semaglutide (Ozempic®) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro®), have shown great results for weight loss. However, these drugs are delivered systemically, resulting in unintended side-effects and require lifelong administration.
Rutgers researchers have identified a promising, more targeted solution employing novel micro-RNA (miRNA) based nanoparticles. Upon delivery, these nanoparticles release their constituent miRNAs, in this case targeting miR-133a, a gene found specifically in adipocytes. This leads to increased expression of thermogenic genes (Prdm16 and Ucp1) and increased mitochondrial biogenesis, resulting in the browning of adipocytes, and leading to a reduction in size of 3D adipocyte spheroids. This nanoparticle formulation results in increased intracellular stability of the delivered miRNAs.
Market Applications:
Advantages:
Publication: https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202400654
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Patent pending. Available for licensing and/or research collaboration. For any business development and other collaborative partnerships, contact: marketingbd@research.rutgers.edu